NEEDS FULFILMENT
The Happiness Agenda aims to address the needs of people that are essential to enhancing happiness for both the short and long term. The Happiness Agenda will discover these needs, create changes that support them, create awareness so that others can support them proactively, and innovate towards ‘happiness’ by satisfying individuals affective, emotional, basic, cognitive and deeper eudaemonic needs.
“We will adopt globally unique and holistic approach to happiness by impacting individual’s basic and higher needs.”
According to the hierarchy of needs (Maslow, 1954), basic needs must be satisfied before higher needs are satisfied. One approach is to opt for addressing basic needs first, then higher needs. However, a mix is the better option.
Provision for basic needs will have an immediate, pragmatic and tangible value for customers. Good customer experience design, as an example, can reduce stress for customers while delivering essential services efficiently easily.
“Positive psychology is about what works, rather than what doesn’t.”
Higher needs, on the other hand, will tend to have more long-term psychological value, as illustrated by the field of Positive Psychology (Seligman & Csikszentmihalyi, 2000), where the focus is on well-being and pleasure (Tiger, 1992). The accepted ‘formula’ for Subjective Well Being, which studies how people experience the quality of their life, encompass both an individual’s sustained sense of satisfaction with their lives, as well as emotional states over time.
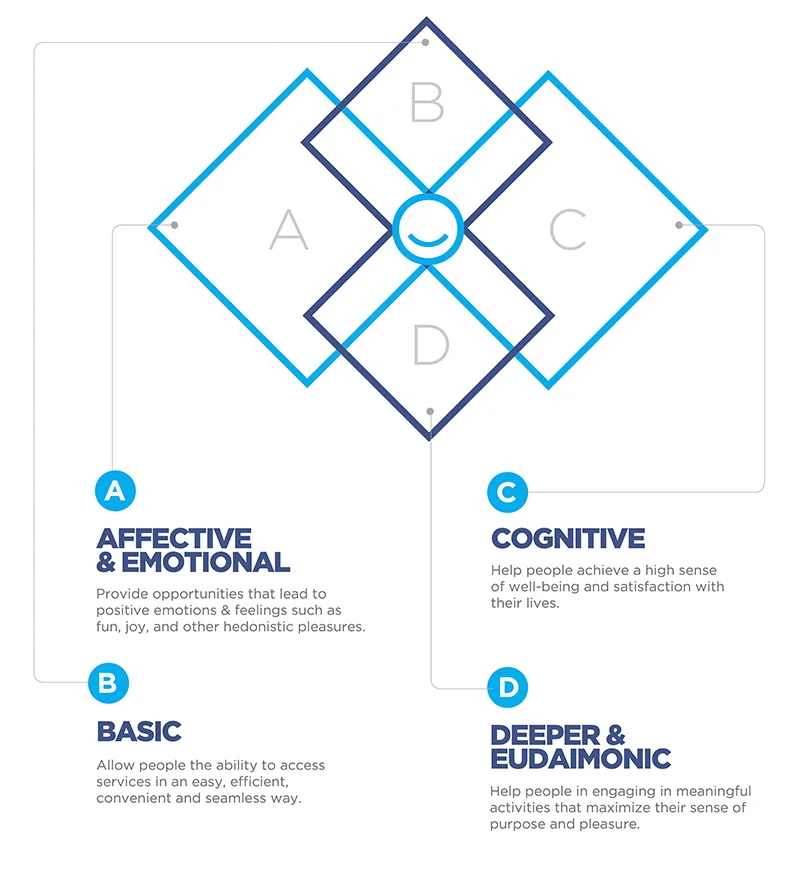
ABCD Of Needs
However, this equation does not make reference to Basic needs, nor the deeper and more profound Eudaimonic needs, which are more about higher meaning and purpose.
Therefore, rather than just addressing basic needs, attending to all the above needs in parallel will yield a better experience for people. The Happiness Agenda aims to increase ‘Happiness’ by satisfying all needs towards a more complete and holistic positive experience.
Affective Needs
People need opportunities to be happy in the moment. We are focusing on making those moments possible.
An individual’s affective, or emotional response to a stimulus, determines how they will react to a situation. Affect is an evaluative system which will lead to an approach-avoidance response (Norman 2003, p. 20). Affect is one component of Subjective Well Being, allowing a person to experience positive emotions.
To satisfy individual’s affective needs, the Happiness Agenda will seek to provide opportunities that lead to positive emotions & feelings such as fun, joy, and other pleasures.
Basic Needs
Satisfying people’s basic service needs is the first duty of a city. Happiness and well-being must build from there.
Living in a city, people have a lot of basic needs regarding services. From water and electricity, to easy access to food, to reliable transportation, to healthcare and an internet connection.
At the most elemental level, people need to know that the service is available, and how to access it. By extension, people need a service that is efficient, convenient, and easy to use. Even greater value is derived from services that are personal, automatic or transparent. Further positive value may be derived by a reduction in cost of time and money.
Satisfying individual’s basic needs provides the platform on which people can stretch a higher frequency of positive emotions and sustained emotional well-being.
The Happiness Agenda seeks to meet people’s basic needs by providing people the ability to access services in an easy, efficient, convenient and seamless way.
Cognitive Needs
People who are satisfied with their quality of life are more likely to feel positive in new situations.
Subjective Well-Being (SWB) is equated to the sum of Affective & Cognitive needs (OECD, 2013), and cognition is a process that is related to assessment, and is for interpretation and understanding. With respect to Well-being, this can be related, for example, to a person’s assessment of their ‘Satisfaction with Life’ (Diener, Emmons, Larson, & Griffin, 1985).
Helping people make positive assessment of their lives in important domains; for example work, health, family, housing & income, can lead to improved overall perception of well-being. The Happiness Agenda therefore seeks to help people achieve a high sense of well-being and satisfaction with their lives, in turn enhancing individuals long-term and short-term happiness.
Deeper Needs
People’s desire to achieve a sense of meaning and purpose in life is a driving force for sustained happiness.
Aside from functional needs, people also have needs associated with deeper meaning and purpose in life (Csikszentmihalyi & Rochberg-Halton, 1981). Individuals who have discovered their own sense of meaning and purpose and more likely to experience a state of ‘flow,’ characterised by intense and joyous focus on a particular task, to the exclusion of all other needs. (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990). Such needs may also be related to people actualising their “daimon” (true self) (Vitterso, 2003), also known as Eudaimonic needs (Huta, 2014).
The Happiness Agenda will aim to support people in engaging and meaningful activities that maximize their sense of purpose and pleasure.